Medicinal cannabis and you
Marijuana, dope, pot, grass, weed, Mary Jane, doobie, bud, ganja, hashish, hash, wacky tobaccy…they’re just some of the common names for cannabis.
Whatever you call it, it’s been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years, until it became a banned or controlled substance in most parts of the world.
But for decades there’s been renewed interest in its use in healthcare, with many countries – including Australia in 2016 – decriminalising it for medicinal use.
Last year alone the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) granted over 25,000 applications from doctors to prescribe cannabis, mostly in the form of an oil.
So let’s weed out some of the facts and explore the use of medicinal cannabis for pain and musculoskeletal conditions.
Is it marijuana or cannabis?
It’s both. They’re just different names for the same plant – marijuana is the commonly used name, cannabis is the scientific name. The preferred name for its use in healthcare is medicinal cannabis, to draw the distinction between medicinal use of cannabis and the illegal, recreational use of marijuana.
The tongue twisters – cannabinoids
It’s a tough word to say – far harder than musculoskeletal! – but an important one when we talk about the properties of cannabis. Cannabinoids are the chemicals found in the cannabis plant. They bind onto specific receptors (CB1 and CB2) on the outside of our cells and can affect things like our mood, appetite, memory and pain sensation.
Cannabis has more than 140 cannabinoids. The two major ones are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). THC is the cannabinoid linked with the sensation of feeling ‘high’ that’s associated with recreational marijuana use.
Cannabinoids also occur naturally in our body (endocannabinoids) and can also be created artificially (synthetic cannabinoids).
How’s it taken?
Medicinal cannabis, both plant-based and synthetic, comes in many forms including oils, capsules, oral sprays and vapours. Smoking isn’t an approved preparation as it can cause damage to the lungs and airways.
Does it work?
At the moment, evidence for its use to treat pain associated with arthritis and musculoskeletal conditions is lacking.
Cannabis has been illegal for so long that we don’t have the thorough, scientific evidence we need about: side effects, which cannabinoids (e.g. THC, CBD or a combination) may be effective, dosages, the best form to use (e.g. oil, capsules etc), the long-term effects, or the health conditions or symptoms it may be beneficial for. Research is emerging, but we need a lot more.
Because of this lack of research, the Australian Rheumatology Association doesn’t support the use of medicinal cannabis for musculoskeletal conditions. Their concern is that we don’t have enough info to ensure cannabis is safe and effective for people with musculoskeletal conditions.
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has also stated that there’s “not enough information to tell whether medicinal cannabis is effective in treating pain associated with arthritis and fibromyalgia”.
Possible side effects
As with any medication – and medicinal cannabis is a medication – it can have side effects. They include: dizziness, confusion, changes in appetite, problems with balance and difficulties concentrating or thinking.
The extent of side effects can vary between people and with the type of medicinal cannabis product being used.
How do I access it?
Unfortunately it’s a complicated process. We aren’t at the stage where a doctor can just write a prescription that you can fill at any chemist. Medicinal cannabis is an unregistered medicine, which means your doctor must be an Authorised Prescriber or must apply for you to have access to it through the TGA’s Special Access Scheme.
But if it’s something you’d like to try, talk with your doctor about whether it’s a possible option for you. Together you can weigh up the risks and benefits for your specific situation.
You need to be aware that medicinal cannabis is not on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS), so if you can access it, you’ll likely have to pay significant costs.
Another option for gaining access to medicinal cannabis is to consult a doctor at a specialised cannabis clinic. This also comes at a price, however it may be an option if your doctor isn’t an authorised prescriber or they’re not well-informed in the use and prescribing of medicinal cannabis.
Driving and medicinal cannabis
If you’re using medicinal cannabis it’s important that you know exactly what’s in it. If you’re taking a product that you’ve obtained through legal prescribers that only contains CBD, you can drive. However if you’re using a product that has any THC in it, whether on its own or in combination with CBD, you can’t drive. It’s currently a criminal offence to drive with any THC in your system.
Talk with your doctor and/or pharmacist for more information.
Interactions with other medications
As with any substance you ingest, there’s the potential for medicinal cannabis to interact with other medications and supplements you’re taking. So before prescribing medicinal cannabis, your doctor will review your current medications to reduce the risk of any negative effects.
However if while using medicinal cannabis you experience any unusual symptoms, discuss these with your doctor.
Finally
For many people the use of medicinal cannabis could be a long way off. And unlike the way it’s often portrayed in the media, it’s unlikely to be a panacea or magic bullet that will cure all ills.
It also won’t work in isolation – you’ll still need to do all of the other things you do to manage your condition and pain, including exercise, managing your weight, mindfulness, managing stress, pacing etc.
The important thing is to be as educated as you can and be open in your discussions with your doctor.
And be aware that cannabis for non-medicinal purposes is still illegal in Australia.
First written and published by Lisa Bywaters, Dec 2020.
For more detailed information about medical cannabis in Australia watch our webinar
Medicinal cannabis in Australia: Weeding out the facts
Dr Richard di Natale, outgoing Senator and former leader of the Australian Greens, and Prof Iain McGregor, Lambert Initiative for Cannabinoid Therapeutics, University of Sydney discuss the use of medicinal cannabis in Australia – what it is, available forms, access issues in Australia and the current evidence for use.
Call our Help Line
If you have questions about things like managing your pain, your musculoskeletal condition, treatment options, COVID-19, telehealth, or accessing services be sure to call our nurses. They’re available weekdays between 9am-5pm on 1800 263 265; email (helpline@msk.org.au) or via Messenger.
More to explore
- Medicinal cannabis to manage chronic pain? We don’t have evidence it works
The Conversation, 23 March 2021 - Current barriers to patient access to medicinal cannabis in Australia
Australian Government, March 2020 - Medicinal cannabis products: Information for consumers
Therapeutic Goods Administration, September 2020 - Medicinal cannabis explained
National Prescribing Service - Lambert Initiative for Cannabinoid Therapeutics
The University of Sydney - Medicinal cannabis
Alcohol and Drug Foundation, October 2020 - ARA Position Statement on the use of medicinal cannabis for musculoskeletal pain
Australian Rheumatology Association, November 2016








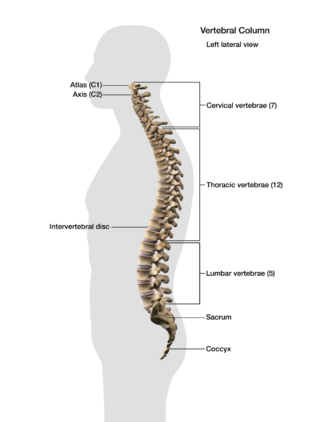 Let’s start with a look at your spine
Let’s start with a look at your spine

















